 swmm
swmm
The EPA Stormwater Management Model (SWMM) is a dynamic rainfall-runoff simulation model used for single-event or long-term (continuous) simulation of the amount and
quality of runoff from mainly urban areas.
The runoff component of SWMM operates on a collection of subcatchment areas that receive precipitation and generate runoff and pollutant loads.
The routing portion of SWMM transports this flow through a system of pipes, channels, storage/treatment devices, pumps, and regulators.
SWMM tracks the quantity and quality of runoff generated within each subcatchment and the flow rate, flow depth and water quality
in each pipe and channel during a simulation period composed of several time steps.
SWMM was first developed in 1971 and has gone through several major updates since then. It continues to be widely used around the world for planning, analysis and design related to stormwater runoff, combined sewers, sanitary sewers and other drainage systems in urban areas, with many applications in non-urban areas as well.
The current implemented version of SWMM in SOLIDOS is version 5.1 .015
This node concentrates all settings related to SWMM, with regard to simulations. Its subnodes contain the settings for the "non-graphical" items of the network, such as time patterns, curves, time series, etc.
In the SWMM node, you can:
-
 Properties - Edit the SWMM properties, listed below
Properties - Edit the SWMM properties, listed below
-
 Calculate - calculate the SWMM network, see command
Calculate - calculate the SWMM network, see command
 SWMMCALC, for more information
SWMMCALC, for more information
-
 Import - imports an INP file from SWMM and draws the network in Model Space, see command
Import - imports an INP file from SWMM and draws the network in Model Space, see command
 SWMMIMPORT, for more information
SWMMIMPORT, for more information
-
 Export - exports a SWMM INP file, see command
Export - exports a SWMM INP file, see command
 SWMMEXPORT, for more information
SWMMEXPORT, for more information
The SWMM node, concentrates the settings that you normally see in Options of the official SWMM program:
- Identification
- Description - Use a friendly description when the item name is not enough
- Name - name of the item
Avoid names that are too long, or that contain the following characters: '*', '>', '<', '/', '\', '"', ':', ';', '|', '=', '`', '#', ',', '?'
- Priority - Information about the current state of the item. It might be:
-
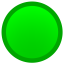 Neutral: no problem
Neutral: no problem
-
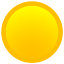 Warning: some problem, but that does not prevent the use or calculation
Warning: some problem, but that does not prevent the use or calculation
-
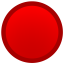 Critical: Some issue that prevents the item from being calculated or used
Critical: Some issue that prevents the item from being calculated or used
- Object Type - informs the object type
- Object
- Auto Calculate - Recalculates the network on any changes made to components
 Note: this can slow down Civil 3D. Please leave this option off.
Note: this can slow down Civil 3D. Please leave this option off.
- It's Calculated - Informs if the network is calculated
- Dates
- Reports Start Date - Date on which reports start
- End Date - Date on which the simulation should end
- Start Date - Date when the simulation starts
- Dry Days - Number of days without rain before the start of the simulation
- End of Street Cleaning - Day of the year when street sweeping operations end
- Report Start Time - Time of day the report starts
- End Time - Time at which the simulation should end
- Start Time - Time of day the simulation starts
- Street Cleaning Starts - Day of the year when street sweeping operations begin
- Import
- Catchment Group - catchment group into which the SWMM catchments will be imported
- Import Vertices from Links - Indicates whether when importing links containing vertices, these will be converted to point devices or ignored
 Note: SWMM allows you to add vertices to links. This is just a visual aid
to be used when the drawing is too dense and the proximity between the nodes makes the link "disappear". Geometrically it shouldn't be considered unless you want to
deliberately use the coordinates of the vertices, because I wanted to represent curved pipes, maybe
Note: SWMM allows you to add vertices to links. This is just a visual aid
to be used when the drawing is too dense and the proximity between the nodes makes the link "disappear". Geometrically it shouldn't be considered unless you want to
deliberately use the coordinates of the vertices, because I wanted to represent curved pipes, maybe
- Links - Table converting INP information to cross sections of links to be imported
 Note: SWMM does not store much information about the typical pipe section.
Note: SWMM does not store much information about the typical pipe section.
Even for standardized sections of the program, the wall thickness is not important for the hydraulic calculation and therefore there is no such property in the SWMM links.
The only place to store some "extra" information is the TAG property. You can use it to store the typical section, or just use the width or height of the section:

See more information in the command
 SWMMIMPORT
SWMMIMPORT
- Nodes - Table converting INP information to cross sections of nodes to be imported
 Note: Similar considerations for nodes. SWMM does not store information about the type of node, which could be a manhole, connection box or manhole. Use the TAG property to differentiate devices as to the typical section before importing into SOLIDOS
Note: Similar considerations for nodes. SWMM does not store information about the type of node, which could be a manhole, connection box or manhole. Use the TAG property to differentiate devices as to the typical section before importing into SOLIDOS
- Network - Network where nodes and links will be imported
 Note: SWMM does not distinguish between subnetworks, so the import can only create one network in SOLIDOS
Note: SWMM does not distinguish between subnetworks, so the import can only create one network in SOLIDOS
SWMM has no surface information. SOLIDOS will infer the top dimensions, but if you have the surface in Civil 3D, enter it in the network properties before importing
- Rotate Structures - Calculates a rotation for structures, based on the longest pipe connected
 Note: for hydraulic calculation, devices rotation is not used. But for geometry, it is.
SOLIDOS can infer rotations based on connected pipes. Check this option to calculate rotation during import
Note: for hydraulic calculation, devices rotation is not used. But for geometry, it is.
SOLIDOS can infer rotations based on connected pipes. Check this option to calculate rotation during import
- Time Increment
- Wet Runoff - The duration of the time step used to calculate subcatchment runoff during periods of rain, or when lake water is still on the surface, or when the LID controls are still seeping or evaporating runoff
- Dry Runoff - The duration of the time step used for runoff calculations (consisting essentially of the accumulation of pollutants) during periods when there is no rain, no water is accumulated and the LID controls are on. dry
- Control Rules Increment - Duration of the time step used to evaluate the control rules
- Routing Increment - Length of time interval used to route flows and water quality constituents through the transport system
- Reports Increment - Time interval for reporting calculated results
- Steady Flow Periods
- Skip Pseudo Stationary Periods - Checking the box Skip periods of constant flow will cause SWMM to continue using the most recently computed transport system flows (instead of computing a new flow solution) whenever the above criteria are met. Using this feature can help speed up simulation run times at the cost of reduced accuracy
- System Flow Tolerance - The percentage difference between total system input and total system output is below the System Flow Tolerance
- Lateral Flow Tolerance - The percentage differences between the current lateral inflow and that of the previous time step for all points in the transport system are below the Lateral Flow Tolerance
- Process Models
- Dynamic Wave
- Inertial Damping - Indicates how the inertial terms in the St. Venant will be treated
- Minimum Area - Minimum surface area used in nodes when calculating changes in water depth
- Forced Main Equation - selects which equation will be used to calculate friction losses during pressurized flow for conduits that have been assigned to a section circular force principal cross
- Elongation Increment - Time interval used to artificially elongate conduits to meet the Courant stability criterion under full flow conditions
- Minimum Increment - Smallest time interval allowed when variable time intervals are used
- Variable Increment - Indicates whether an internally computed variable time interval should be used in each routing period and select an adjustment (or safety) factor to apply to this time interval
- Flow Limit - Supercritical flow definition template
- Surcharge Method - Handles surcharge conditions. The Extran option uses a variation of the surcharge algorithm from previous versions of SWMM to update the nodal heads when all connecting links become full. The Slot option uses a Preissmann Slot to add a small amount virtual top surface width ade for full flow pipes so the normal SWMM procedure for updating nodal heads can continue to be used
- Number of Threads - This selects the number of parallel computing threads to use on machines equipped with multi-core processors
- Attempts - Maximum number of attempts that SWMM uses at each time step to achieve convergence when updating hydraulic heads on conveyor system nodes
- Load Tolerance - When the difference in the calculated load at each node between successive trials is below this value, the flow solution for the current time step is assumed to have converged
- General Options
- Minimum slope - Minimum value allowed for the slope of a conduit
- Infiltration Modeling - Standard method used to model rainfall infiltration into the upper ground zone of Subcatchments
- Flow Propagation Model - Method used to route flows through the transport system
- Allow Flooding - Allow excess water to pool on top of the nodes and be reintroduced into the system as conditions permit
- Reports
- Catchments - Show the Catchment report for:
- None - does not show the catchments in the report
- All - shows all catchments in the report
- Some - show only the marked catchments (see Show in Report in Catchment properties)
- Continuity Errors - Continuity Errors
- Links - Show the report links to:
- None - does not show the Links in the report
- All - shows all links in the report
- Some - show only marked links (see Show in Report in links properties)
- Nodes - Show the report of Nodes for:
- None - does not show nodes in the report
- All - shows all nodes in the report
- Some - show only marked nodes (see Show in Report in node properties)
- Node Depth - Node Depth
- Input Report - Check this option if you want the Simulation Status Report to list a summary of project input data
- Control Actions Report - Check this option if you want the Simulation Status Report to list all discrete control actions taken by Control Rules associated with a project (continuous modulated control actions are not listed). This option should only be used for short term simulation
- Output Report - Show program output report
- Average Results - Check this option if you want the average of the results of all routing time steps that fall within a reporting time step to be reported instead of the instantaneous point results that occur at the end of the reporting time step
- Flow Routing - Flow Routing
The properties of "physical" items such as Nodes, catchments, and pipes, must be viewed in the properties of these items, using the command
 SPROPS, or using the
Properties Tab of Toolspace
SPROPS, or using the
Properties Tab of Toolspace

![]() SPROPS, or using the
Properties Tab of Toolspace
SPROPS, or using the
Properties Tab of Toolspace