SWMM - Computational Methods - Groundwater
Shown below is a sketch definition of the two-zone groundwater model that is used in SWMM. The upper zone is unsaturated with a variable moisture content of ?. The lower zone is fully saturated and therefore its moisture content is fixed in soil porosity.
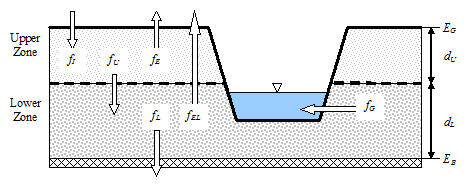
The flows shown in the figure, expressed as volume per unit area per unit time, consist of the following:
- fI - Surface infiltration
- fEU - upper zone evapotranspiration, which is a fixed fraction of unused surface evaporation
- fU - percolation from the upper zone to the lower zone, which depends on the moisture content of the upper zone ? and the depth dU
- FEL - Evapotranspiration of the lower zone, which is a function of the depth of the upper zone dU
- fL - infiltration of the lower zone for deep groundwater, which depends on the depth of the lower zone dL
- fG - Lateral inflow of groundwater to the transmission network that depends on the depth of the lower zone dL, as well as the depths of the channel or reception node.
After calculating the water fluxes that exist during a given time step, a mass balance is written for the change in the volume of water stored in each zone so that a new water table depth and moisture content of the unsaturated zone can be calculated for the next time step.

