 SWMM - Aquifers
SWMM - Aquifers
Aquifers are underground zones used to model the vertical movement of water that infiltrates the Subcatchments above them.
They also allow the infiltration of groundwater into the drainage system, or the exfiltration of surface water from the drainage system, depending on the existing hydraulic gradient.
Aquifers are only needed in models that need to explicitly explain groundwater exchange with the drainage system or establish baseflow and recession curves in natural channels and non-urban systems.
The parameters of an aquifer object can be shared by several Subcatchments, but there is no groundwater exchange between the Subcatchments.
A drainage system node can exchange groundwater with more than one subcatchment.
Aquifers are represented using two zones - an unsaturated zone and a saturated zone.
Its behavior is characterized using parameters such as soil porosity, hydraulic Conductivity, evapotranspiration depth, bottom elevation and rate of loss to deep groundwater.
In addition, the initial water table rise and the initial moisture content of the unsaturated zone must be provided.
Aquifers are connected to subcatchments and drainage system nodes as defined in the Groundwater category of a subcatchment .
This category also contains parameters that govern the rate of groundwater flow between the saturated zone of the aquifer and the node of the drainage system.
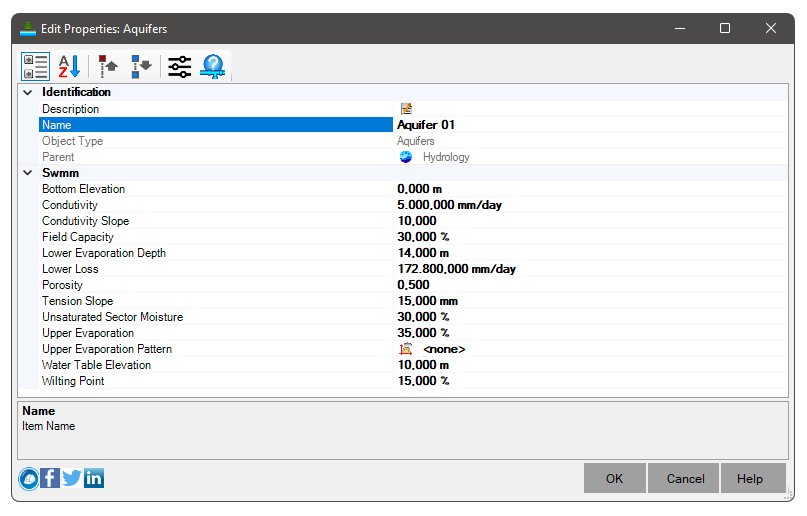
To define an aquifer, the following parameters must be informed:
- Identification
- Description - Use a friendly description when the item name is not enough
- Name - name of the item
Avoid names that are too long, or that contain the following characters: '*', '>', '<', '/', '\', '"', ':', ';', '|', '=', '`', '#', ',', '?'
- Priority - Information about the current state of the item. It might be:
 Neutral: no problem
Neutral: no problem Critical: Some issue that prevents the item from being calculated or used
Critical: Some issue that prevents the item from being calculated or used
- SWMM
- Field Capacity - Soil moisture content after all free water has drained
- Hydraulic Conductivity - Mean slope of logarithmic Conductivity versus soil moisture deficit
- Conductivity Slope - Average slope of logarithmic Conductivity versus soil moisture deficit
- Curve Slope - Average slope of the soil stress curve versus soil moisture content
- Elevation of the Fund - Elevation of the aquifer bottom
- Upper Evaporation - Fraction of total evaporation available for evapotranspiration in the upper unsaturated zone
- Static Level - Water table rise in the aquifer at the start of the simulation
- Evaporation Pattern - The name of a monthly time pattern used to adjust the Upper Evaporation Fraction for different months of the year
- Wilting Point - Soil moisture content in which plants cannot survive
- Porosity - The volume of pore space in relation to the total soil volume
- Evaporation Depth - Maximum depth in the lower saturated zone over which evapotranspiration can occur
- Percolation Rate - Percolation rate for deep groundwater when the water table reaches the soil surface
- Unsaturated Zone Moisture - Moisture content of the upper unsaturated zone of the aquifer at the start of the simulation
