 EPANET - Pipe
EPANET - Pipe
The pipes lead the water from one point to another in the network.
EPANET assumes that all pipes are full at all times.
The direction of flow is from end at the highest head (internal energy per weight of water) to the bottom head.
In addition to the shared properties of EPANET links, pipes also have the following properties:
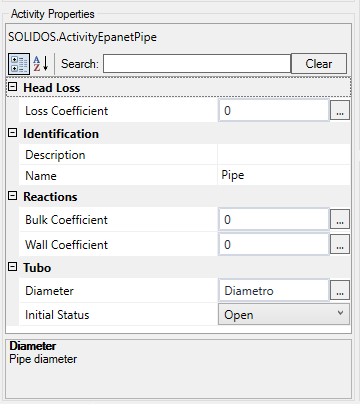
- Head Loss
- Loss Coefficient (LossCoefficient, Double) - Minor unitless loss coefficient that applies when the valve is fully open
Minor losses caused by bends and connections can also be accounted for by assigning the pipe a lower loss coefficient.
- Pipe
- Coefficient of Use (CUtil, Double) - Indicates that the pipe can receive building connections or not
It is used to calculate the Fictitious Length, given by:
Fictitious Length = ((3D Length) * (Usage Coefficient))
Used to calculate the Base Demand, when the network has data to calculate
the demand in motion
Pipes that are part of water mains usually do not have building connections so they are not included in the calculation of the base demand of the nodes connected to it. In this case the
duty utilization coefficient zero
Valves and Pumps, despite being modeled in linear devices, do not enter into the calculation
from running demand from the network
- Diameter (Diameter, Double) - Diameter of the pipe, mandatory property, assigned by the Constructor (see below)
- Initial State (PipeStatus, Enum) - Determines if the pipe is initially
- Reactions
- Wall Coefficient (WallCoefficient) - Coefficient of reaction of the wall to the pipe. Use a positive value for growth and a negative value for decay
- Bulk Coefficient (BulkCoefficient) - Mass reaction coefficient for the pipe.
Use a positive value for growth and a negative value for decay
- Calculations - are filled in by the command
 EPANETCALC, when it succeeds in the simulation
EPANETCALC, when it succeeds in the simulation
- Reaction Rate (ReactionRate) - Reaction rate
- Calculated Speed (CalcVelocity) - Calculated speed for the link
- Leakage (Leakage) - The rate at which a pipe leaks at a given point in time
- Leakage
- Leak Expansion Ratio (LeakExpan) - Leakage expansion ratio (mm² per unit of pressure)
- Leakage Area (LeakArea) - Pipe leakage area (mm² per 100 units of length)
For a device to be recognized as an EPANET pipe, the
 Constructor
must contain an activity
Constructor
must contain an activity
 Pipe:
Pipe:
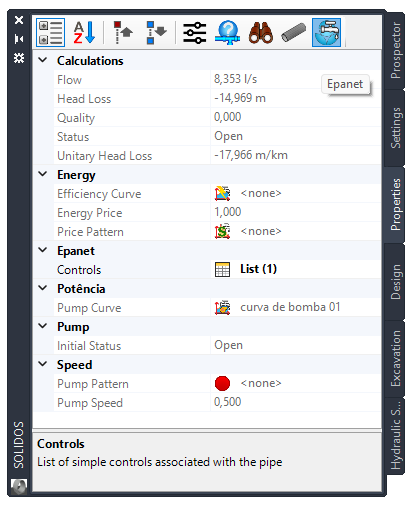
In the properties frame:
To view the pipe properties, click the icon
 in the Properties Tab or in the command
in the Properties Tab or in the command
 SPROPS:
SPROPS:
![]() Constructor
must contain an activity
Constructor
must contain an activity
![]() Pipe:
Pipe:


![]() in the Properties Tab or in the command
in the Properties Tab or in the command
![]() SPROPS:
SPROPS:
