 EPANET - Valve
EPANET - Valve
Valves are used to control pressure or flow at a specific point in the network.
Main features:
- Shut-off valves (gate) and check valves (no return), which completely open or close the pipes, are not considered separate components of the valve, but are included as a property of the pipe they are placed in (see Pipe Properties).
The different types of valves include:
- PRV (pressure reducing valve)
- PSV (pressure sustaining valve)
- PBV (pressure breaker valve)
- FCV (flow control valve)
- TCV (throttle control valve)
- GPV (general purpose valve) - can be used to represent a link where the flow - head loss relationship is provided by the user rather than following one of the standard hydraulic formulas.
- Each type of valve has a different type of configuration parameter that describes its operating point:
- pressure for PRVs, PSVs and PBVs
- flow for FCVs
- loss coefficient for TCVs
- head loss curve for GPVs and PCVs
- Valves can have their control status overridden by specifying that they are fully open or fully closed.
- The status of a valve and its configuration can be changed during the simulation using the controls.
To restore a valve's control status after its status has been changed to open or closed, use a control that specifies a value for the valve setting
- Due to the ways in which valves are modeled, the following rules apply when adding valves to a network:
- PRVs cannot share the same output node or be daisy chained
- Two PSVs cannot share the same input node or be connected in series
- The PSV cannot be connected to the output node of a PRV
- a PRV, PSV, or FCV cannot be connected directly to an
 reservoir or
reservoir or
 tank
(use a
tank
(use a
 Pipe to separate the two)
Pipe to separate the two)
In addition to the shared properties of EPANET links, valves also have the following properties:
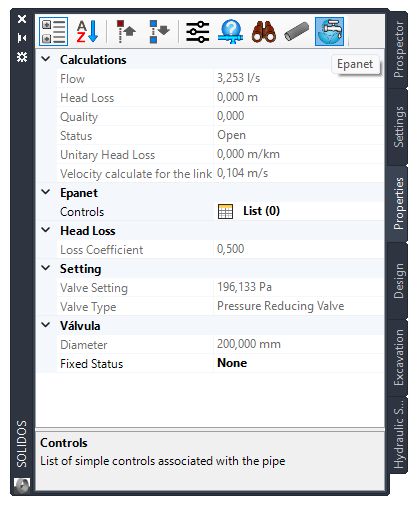
- Calculations
- Calculated Speed - Calculated speed for the link
- Head Loss
- Loss Coefficient - Minor unitless loss coefficient that applies when the valve is fully open
- Head Loss Curve -
 Head Loss curve describing the valve type of 'General Purpose Valve'
Head Loss curve describing the valve type of 'General Purpose Valve'
- Configuration
- Valve Setting - A mandatory parameter that describes the operational configuration of the valve
Note: this parameter has a unit of measure so in Constructor, you must put the value in the SI unit, or imperial, depending on the settings
of Civil 3D unit:
- PRV (pressure reducing valve)
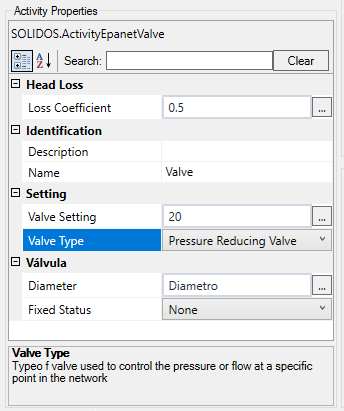
In this case, the unit of measurement is for pressure. In SI, pressure is given in kgf/m² so the value 20 in the image is 20 kgf/m²
If Civil 3D was in imperial units, the value would be 20 psi
- PSV (pressure sustaining valve), kgf/m² or psi
- PBV (pressure breaker valve), kgf/m² or psi
- FCV (flow control valve), liters per second (l/s) or cubic feet per second (cfs or ft³/s)
- TCV (throttle control valve), unitless
- GPV (general purpose valve), informed in the field head loss curve
- PCV (positional control valve), informed in the field head loss curve
- Valve Type - Type of valve used to control pressure or flow at a specific point in the network
- Valve
- Diameter - Diameter
- Fixed Status - Status of the valve at the start of the simulation.
If set to OPEN or CLOSED, the valve's control setting is ignored and the valve behaves as an open or closed link, respectively. If set to NONE then the valve will behave as intended
To view the properties of the valve, click the icon
 in the Properties Tab or in the command
in the Properties Tab or in the command
 SPROPS:
SPROPS:

![]() in the Properties Tab or in the command
in the Properties Tab or in the command
![]() SPROPS:
SPROPS:
