Reservoirs are nodes that represent an external infinite source or sink of water for the network. They are used to model things like lakes, rivers, underground aquifers, and connections to other systems. Reservoirs can also serve as points of water quality sources.
The main inlet properties of a reservoir are its hydraulic head and initial water quality.
As a reservoir is a boundary point for a network, its depth and water quality cannot be affected by what happens within the network.
Therefore, it has no computed output properties. However, its depth can vary over time by assigning an ![]() time pattern to it.
time pattern to it.
In addition to the shared properties of EPANET Nodes, reservoirs also have the following properties:
Obviously, the entire reservoir is not modeled in the Constructor, since it depends on the topography anyway. In the case of the reservoir, model the water intake:
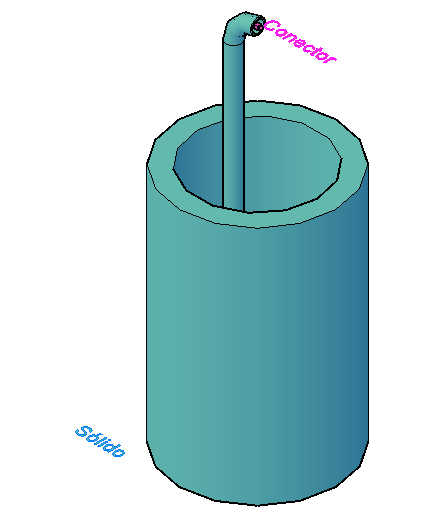
Note the point marked "Connector" is the elevation of the water intake shown in the properties frame above
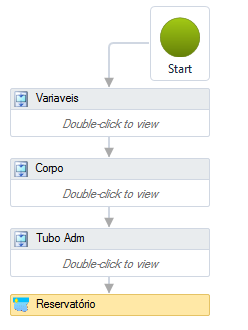
For a device to be recognized as an EPANET reservoir, the ![]() Constructor
must contain an activity
Constructor
must contain an activity ![]() Reservoir:
Reservoir:
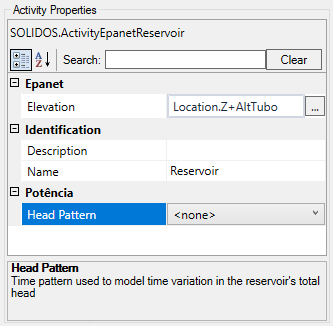
In the properties frame:
To view the reservoir properties, click the icon
![]() in the Properties Tab or in the command
in the Properties Tab or in the command ![]() SPROPS:
SPROPS:
