 EPANET - Pump
EPANET - Pump
Pumps are devices that transmit energy to a fluid, thus increasing its hydraulic head.
Main features:
- The main input parameter of a pump is the pump curve (the combination of head and flows the pump can produce)
- Instead of a pump curve, the pump can be represented as a constant power device
- The main output parameters are flow and load gain
- Flow through a pump is unidirectional. If the system requires more pressure than the pump can produce, the pump is turned off. If more flow is required, the pump curve is extrapolated to produce flow, even if negative pressure results. In both cases, a warning message is issued
- Pumps can be turned on and off at preset times, when tank levels fall below or above certain setpoints, or when nodal pressures fall below or above certain setpoints through the use of controls and patterns of time
- Variable speed pumps can also be considered by specifying that their speed setting be changed under these same types of conditions. By default, the original pump curve supplied to the program has a relative speed setting of 1. If the pump speed doubles, the relative setting would be 2; if run at half speed the relative setting is 0.5 and so on
- EPANET can also calculate the energy consumption and cost of a pump. Specific pump efficiency curves and energy pricing parameters can be provided or global energy options will be used
In addition to the shared properties of EPANET links, pumps also have the following properties:
- pump
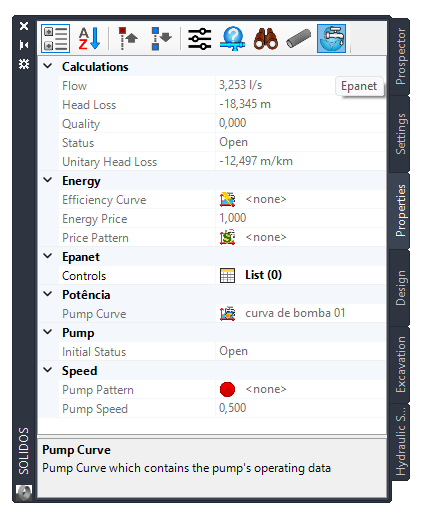
- Initial Status - State of the pump (open or closed) at the beginning of the simulation period
- Energy
- Efficiency Curve -
 Efficiency curve representing the efficiency of the pump run-of-water as a function of the flow rate
Efficiency curve representing the efficiency of the pump run-of-water as a function of the flow rate
- Price Pattern -
 Time pattern used to describe the change in energy price throughout the day
Time pattern used to describe the change in energy price throughout the day
- Energy Price - The average or nominal price of energy in currency units per kw-hour. Only used to calculate cost of energy usage
- Power
- Pump Curve -
 Pump curve which contains the operating data of the pump
Pump curve which contains the operating data of the pump
- Pump Power - Power supplied by the pump (kw). Assumes the pump delivers the same amount of power no matter what the flow is
- Speed
- Pump Pattern -
 Pump pattern used to control pump operation
Pump pattern used to control pump operation
- Pump Speed - The relative pump speed setting
A speed setting of 1.2 implies that the pump rotation speed is 20% higher than the normal setting
To view the pump properties, click the icon
 in the Properties Tab or in the command
in the Properties Tab or in the command  SPROPS:
SPROPS:
![]() in the Properties Tab or in the command
in the Properties Tab or in the command ![]() SPROPS:
SPROPS:
