 STABLESTYLES
STABLESTYLES
The command
 STABLESTYLES creates and edits table styles for tables and reports
STABLESTYLES creates and edits table styles for tables and reports
To use, call STABLESTYLES from the command line, menu, toolbar, in the Ribbon choose the style you want to edit:

On this screen you can:
-
 New - Create a new style
New - Create a new style
-
 Delete - Delete selected styles if not in use
Delete - Delete selected styles if not in use
-
 Edit - Edit the selected style
Edit - Edit the selected style
-
 Copy - Copy and edit the selected table style
Copy - Copy and edit the selected table style
-
 Pick - select on the model space an item that has the style you want to edit
Pick - select on the model space an item that has the style you want to edit
A table style is actually a template for choosing columns, properties etc, for extracting data from devices, catchments or even networks.
Below, an example:
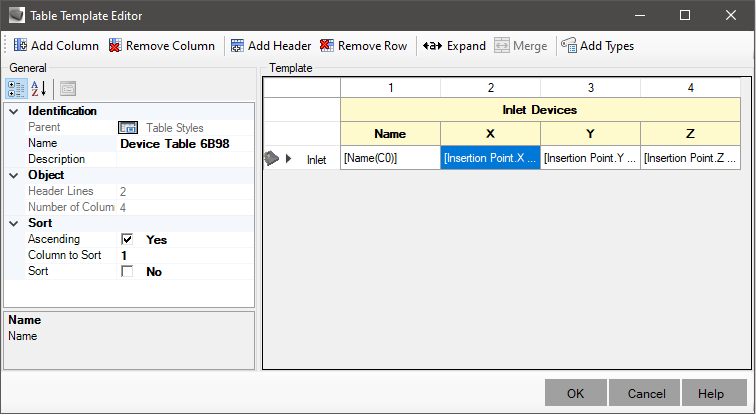
On the screen, at the top, you can see the following buttons:
-
 Add Columns - To add columns to the template
Add Columns - To add columns to the template
After adding some columns, you can add header rows and data rows
-
 Remove Columns Removes selected columns
Remove Columns Removes selected columns
-
 Add Header - to add lines to the header
Add Header - to add lines to the header
In the image above, the cells with a yellow background are the headers, and the ones with a white background are the rows of data.
The header will contain any kind of static text and also allows merging the title cells, giving a better final presentation.
In the example, the table title is Pipe table and the entire row is merged
-
 Remove Row - Removes selected rows, whether headers or data
Remove Row - Removes selected rows, whether headers or data
-
 Expand - Expands the columns of the editor.
Note, it does not affect the resulting table drawn in CAD or exported
Expand - Expands the columns of the editor.
Note, it does not affect the resulting table drawn in CAD or exported
-
 Merge - Merges or unmerges the selected cells.
Merge - Merges or unmerges the selected cells.
Note: Only header cells can be merged as the number of lines of data is changeable
-
 Column Visible - toggles the state of the column:
Column Visible - toggles the state of the column:
-
 Checked - means the column will be shown in the final result
Checked - means the column will be shown in the final result
-
 Unchecked - means the column will not be shown in the final result
Unchecked - means the column will not be shown in the final result
The purpose of this column is to allow the addition of an auxiliary column, which allows ordering the lines of the final table, when
this column need not appear
-
 Add Types - Add element type filter row in table
Add Types - Add element type filter row in table
Note, some types are "generic", for example: Device is generic because it is for linear, or point, device.
"Point Device" is generic as it serves for box or PV.
Then choose a filter suitable for the type of table you want to generate.
Clicking this button will display a screen like this:

Choose the device type and click OK
-
 Filter - Creates/Edits a filter for the selected line
Filter - Creates/Edits a filter for the selected line
To use, select a line that fills in values (the ones with an icon) and click the Filter button. Will be called the
Filter Editor, where you can create an expression to further filter the
items that can be listed on the line

-
 Sum Row - Adds a calculated data row that can sum quantities
Sum Row - Adds a calculated data row that can sum quantities
By adding a summation line, you can add excavation for example, or length of pipes per section
Note that it is possible to add one more filter to items selected by the report or table. Like this,
pipes can be quantified separately:

In the example above, the 2D lengths of the tubes whose section is equal to "BSTC 100 cm" will be added.
In the complete table, one can add similar lines to add up the remaining sizes:

A possible result will be:

-
 Hydraulic Sections in design - makes it possible to list the results of the tab Hydraulic Sections
for the beginning of the project (dimensioning). applies to
Hydraulic Sections in design - makes it possible to list the results of the tab Hydraulic Sections
for the beginning of the project (dimensioning). applies to
 longitudinal gravity devices only
longitudinal gravity devices only
-
 Hydraulic Sections in design - makes it possible to list the results of the tab Hydraulic Sections
to the end of the project (verification). applies to
Hydraulic Sections in design - makes it possible to list the results of the tab Hydraulic Sections
to the end of the project (verification). applies to
 longitudinal gravity devices only
longitudinal gravity devices only
-
 Points - makes it possible to list the points of
Points - makes it possible to list the points of
 longitudinal devices
longitudinal devices
-
 Input Device - in styles of
Input Device - in styles of
 device tables, when the template line shows information for
device tables, when the template line shows information for
 linear devices or
linear devices or
 longitudinal devices, it is possible to show information about the device
plugged into device input
longitudinal devices, it is possible to show information about the device
plugged into device input
-
 Output Device - in styles of
Output Device - in styles of
 device tables, when the template line shows information for
device tables, when the template line shows information for
 linear devices or
linear devices or
 longitudinal devices, it is possible to show information about the device
plugged into device output
longitudinal devices, it is possible to show information about the device
plugged into device output
-
 Current Device - in styles of
Current Device - in styles of
 device tables, when the template line shows information for
device tables, when the template line shows information for
 linear devices or
linear devices or
 longitudinal devices, and the cell has information about the input device
or output click to be able to add linear device properties
longitudinal devices, and the cell has information about the input device
or output click to be able to add linear device properties
-
 Excavation - in styles of
Excavation - in styles of
 device tables, when the template line shows information for
device tables, when the template line shows information for
 linear devices or
linear devices or
 longitudinal devices, and the cell has information about the excavation
from the device ditch
longitudinal devices, and the cell has information about the excavation
from the device ditch
-
 Copy Line - Clones the current property row, making it possible to choose another type of item
Copy Line - Clones the current property row, making it possible to choose another type of item
-
 New!!!: A table in AutoCAD can have a title, header, and data. These can have different styles, as shown in the TABLESTYLE command, native to AutoCAD:
New!!!: A table in AutoCAD can have a title, header, and data. These can have different styles, as shown in the TABLESTYLE command, native to AutoCAD:
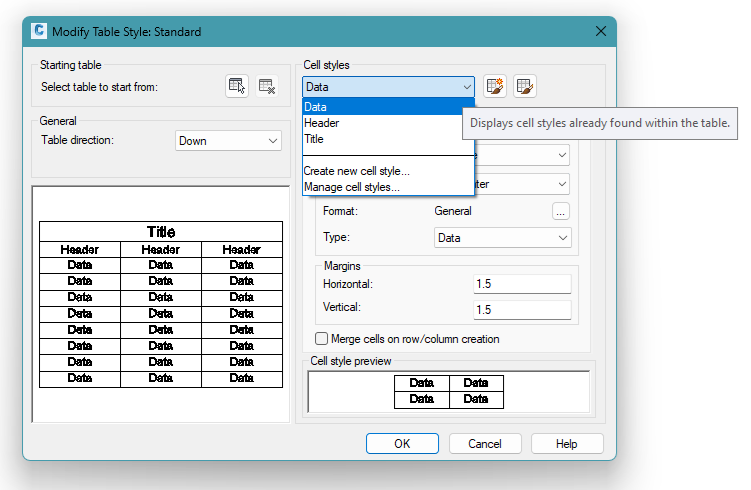
When SOLIDOS fills the table data, it will look for formats, according to the style you created:

When you look at the table for maid, you will see this configuration here:
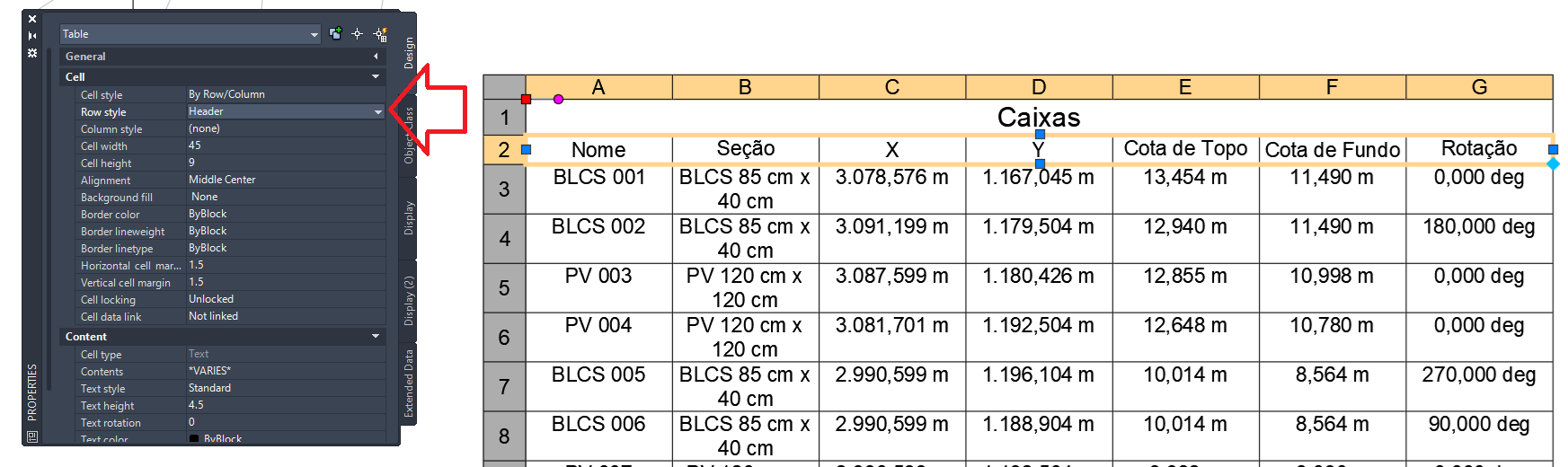
Assim, you will be able to enable line breaks in the table and make the title/header appear in all sub tables
After choosing an object type, it is necessary to add the macro that defines the property and formatting expected for it. To do this, double-click on the cell:

The Macro Editor will open:
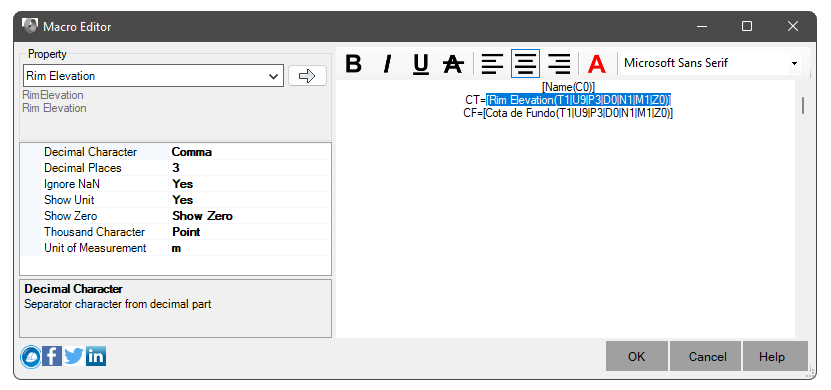
Choose the property, formatting and click the button
 Note: Device tables may require cross-referencing. This happens when linear device data does not show data referring to point devices.
For example: Nodes want a table of pipes that shows data from the PV insertion point, or even data from its Hydraulic Design (precipitation, contribution area, etc).
In this situation, use the buttons
Note: Device tables may require cross-referencing. This happens when linear device data does not show data referring to point devices.
For example: Nodes want a table of pipes that shows data from the PV insertion point, or even data from its Hydraulic Design (precipitation, contribution area, etc).
In this situation, use the buttons
 Input Device,
Input Device,
 Output Device. You will notice that the cell icon will change. This means the properties will be read
on the upstream or downstream PV, not on the pipe itself.
Output Device. You will notice that the cell icon will change. This means the properties will be read
on the upstream or downstream PV, not on the pipe itself.
 Note: Linear devices (pipes, gutters, etc) when they have excavation calculated, can also show this data in the table.
In this case, it will be necessary to click the button
Note: Linear devices (pipes, gutters, etc) when they have excavation calculated, can also show this data in the table.
In this case, it will be necessary to click the button
 Excavation and add any columns you want.
Excavation and add any columns you want.
To exemplify the two situations above, consider the style below:

Columns and 5 show upstream and downstream PV data respectively, while columns 1, 2 and 3 show pipe data. In the row below, columns 5, 6 and 7
show data from the excavated trench. Note that the excavated trench has several sections. Therefore, multiple lines are added. A possible result of the above style:

 Note: When creating a table, you will be asked to select the elements that can be included in the table listing.
If the type is not present in one of the rows of data in the table template, or is not a type
child of the types listed in the template, it will be ignored.
If it matches more than one row of data, the element may appear more than once in the resulting table.
Note: When creating a table, you will be asked to select the elements that can be included in the table listing.
If the type is not present in one of the rows of data in the table template, or is not a type
child of the types listed in the template, it will be ignored.
If it matches more than one row of data, the element may appear more than once in the resulting table.
![]() STABLESTYLES creates and edits table styles for tables and reports
STABLESTYLES creates and edits table styles for tables and reports












![]()
![]() Note: Device tables may require cross-referencing. This happens when linear device data does not show data referring to point devices.
For example: Nodes want a table of pipes that shows data from the PV insertion point, or even data from its Hydraulic Design (precipitation, contribution area, etc).
In this situation, use the buttons
Note: Device tables may require cross-referencing. This happens when linear device data does not show data referring to point devices.
For example: Nodes want a table of pipes that shows data from the PV insertion point, or even data from its Hydraulic Design (precipitation, contribution area, etc).
In this situation, use the buttons
![]() Input Device,
Input Device,
![]() Output Device. You will notice that the cell icon will change. This means the properties will be read
on the upstream or downstream PV, not on the pipe itself.
Output Device. You will notice that the cell icon will change. This means the properties will be read
on the upstream or downstream PV, not on the pipe itself.
![]() Note: Linear devices (pipes, gutters, etc) when they have excavation calculated, can also show this data in the table.
In this case, it will be necessary to click the button
Note: Linear devices (pipes, gutters, etc) when they have excavation calculated, can also show this data in the table.
In this case, it will be necessary to click the button
![]() Excavation and add any columns you want.
Excavation and add any columns you want.


![]() Note: When creating a table, you will be asked to select the elements that can be included in the table listing.
If the type is not present in one of the rows of data in the table template, or is not a type
child of the types listed in the template, it will be ignored.
If it matches more than one row of data, the element may appear more than once in the resulting table.
Note: When creating a table, you will be asked to select the elements that can be included in the table listing.
If the type is not present in one of the rows of data in the table template, or is not a type
child of the types listed in the template, it will be ignored.
If it matches more than one row of data, the element may appear more than once in the resulting table.