SOLIDOS Modeler - Calculate Target
 Calculate Target - calculates a point on a reference Curve and
a target point on another curve:
Calculate Target - calculates a point on a reference Curve and
a target point on another curve:

The Calculate Target activity has the following properties:
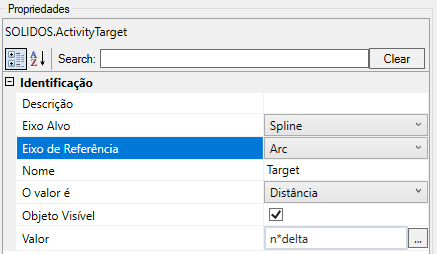
- Identification
- Name - name of the activity
The point name must follow the naming rules
- Reference Axis - Indicates which curve will be used to calculate the base point
- Target Axis - Indicates which curve will be used to calculate the target point
- Object Visible - indicates whether or not the point should be drawn in the preview
- Value is - indicates what kind of value is provided to calculate the point, it can be:
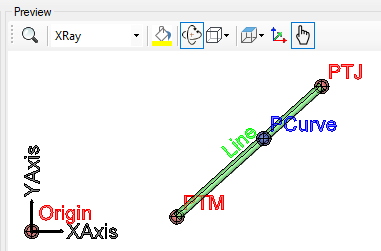
- Distance - 3D distance over the line, starting from the beginning of the line.
In the example above, I used a VB expression:
Line.
Length / 2
- 2D Distance - It works similarly to the Distance option, except that the distance is taken into account when projecting the curve in the XY plane
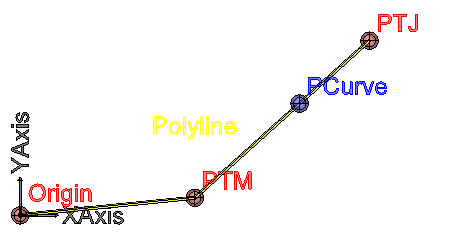
- Parameter - is a number, whose integer part refers to the vertex number and the fractional part refers to the percentage of the segment following this vertex
in a polyline, the parameter 1.55 would be in the second segment (the first segment has ZERO index), counting 55% of its length:
- Point - another point, not necessarily on the curve
The closest point to the curve will be calculated.

- Value - a VB expression that provides value to calculate the point on the curve
Note the 'Value is' field. The expression must return the same data type
After the point has been calculated, it is possible to obtain the following properties:
- IsValid - a true/false value (Boolean) that indicates whether the base point (BasePoint) and target point (TargetPoint) could be calculated
- BasePoint - an
 point over the reference curve
point over the reference curve
- TargetPoint - an
 point over the target curve
point over the target curve
- Offset - the distance in the XY plane between the BasePoint and the TargetPoint, measured perpendicular to the tangent vector of the projection in the XY plane of the reference curve
A positive value indicates that the TargetPoint is to the right of the reference axis
A negative value indicates that the TargetPoint is to the left of the reference axis
- DeltaElevation - the vertical distance between the BasePoint and the TargetPoint
DeltaElevation = TargetPoint.Z - BasePoint.Z
A positive value indicates that the TargetPoint is above the reference axis
A negative value indicates that the TargetPoint is below the reference axis
An example of using this tool:
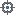
In the image above, the  yellow arc is in the XY plane, while the
yellow arc is in the XY plane, while the  Spline is three-dimensional
Spline is three-dimensional
To model a solid as if it were a Civil 3D corridor, you must create a looping, which calculates several sections along the reference axis
and use the tool  Transition between them. Consider this example:
Transition between them. Consider this example:
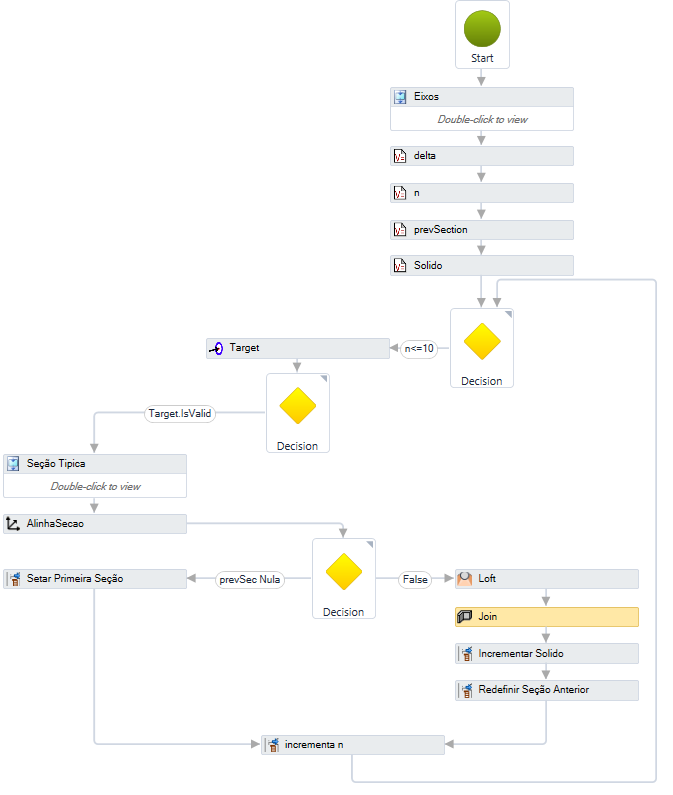
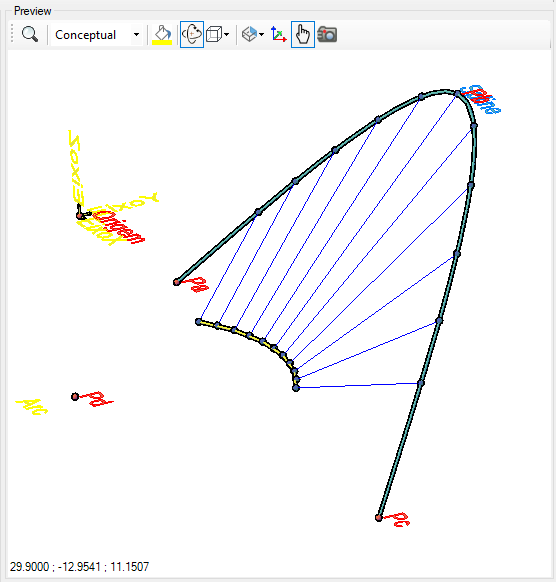
The flow executes the solid below:

The flow executes:
- Create a reference axis (Arc)
- Create a target axis (Spline)
- Initialize the variables:
- delta = Arc.length / 10
- n = 0
- prevSection = Nothing
- Solid = Nothing
- If n ≤ 10, run:
- Calculates the Target:
- Calculates the base point on the Arc
curve
- Calculates the target point on the Spline
curve
- Create a typical section, which uses the value of Target.Offset and Target.DeltaElevation
- Aligns the typical section at the point Target.BasePoint and creates the curve AlinhaSecao
- Tests if the prevSection is null and:
- If it is null, define: prevSection = AlinhaSecao
- If the prevSevtion exists, then:
- Creates the Loft transition between prevSection and AlinhaSecao
- Joins the Solid variable with the Loft transition, creating the Join
- Adds the Join to the Solid
variable
- Define prevSection = AlinhaSecao (to use in the next looping)
- Increment n, making n= n + 1
- Return to step 4
If the text gets too big/small, or the sphere that represents the point gets too big or small, use the buttons ( A, a,  ,
,  ) at the top of the screen to change the preview
) at the top of the screen to change the preview
Properties (for use in VB expressions)
implements the properties of points in addition to the properties listed above
Methods (for use in VB expressions)
implements the methods of the points
![]() Calculate Target - calculates a point on a reference Curve and
a target point on another curve:
Calculate Target - calculates a point on a reference Curve and
a target point on another curve:






![]() yellow arc is in the XY plane, while the
yellow arc is in the XY plane, while the ![]() Spline is three-dimensional
Spline is three-dimensional
![]() Transition between them. Consider this example:
Transition between them. Consider this example:


![]() ,
, ![]() ) at the top of the screen to change the preview
) at the top of the screen to change the preview