 SWMM - Nodes - Storage
SWMM - Nodes - Storage
Storage units (reservoirs) are drainage system nodes that provide storage volume.
Physically, they can represent storage facilities as small as a Catchment or as large as a lake.
The volumetric properties of a storage unit are described by a function or table of surface area versus height.
In addition to receiving inflows and discharging outflows to other nodes in the Drainage Network, storage nodes can also lose water through surface evaporation and infiltration into the native soil.
In addition to the SWMM node properties, storage units also have the following properties:

- Loss of Infiltration
- Hydraulic Conductivity - Hydraulic Conductivity for fully saturated soil
- Initial Deficit - Fraction of soil volume that is initially dry
- Suction Potential - Mean capillary suction value of the soil along the wetting front
- SWMM
- Bottom Elevation - Elevation of the bottom of the node (radier elevation)
It must be associated with the property of the constructor that manages the device's Sump Elevation, for example:

- Evaporation Fraction - The fraction of potential evaporation from surface water from the storage unit that is actually realized
- Initial Depth - Initial depth of water in the storage unit at the start of the simulation
- Maximum Depth - Maximum depth of the storage unit
- Depth Overload - Additional water depth beyond the maximum allowable depth before the junction floods
- Storage Type
- Storage Type - Method for describing how the surface area of the storage unit varies with water depth
It can be of two types:
- Tabular - Describes the surface area of the storage unit varying with depth in a curve
- Storage Curve - Name of the storage curve that contains the relationship between surface area and storage depth
- Functional - Describes the surface area of the storage unit varying with water depth by the relationship:
Area = A * Depth ^ B + C
- Coefficient - A value in the functional relationship between surface area and storage depth
- Constant - C value in the functional relationship between surface area and storage depth.
- Exponent - B value in the functional relationship between surface area and storage depth.
- Cylindrical - Storage unit has vertical sides and an elliptical base
The surface area equation is:
Area = (π / 4) * ( L * W )
Where:
L = length of the main axis of the base
W = width of the minor axis of the base
- Conical -The storage unit is shaped like a truncated elliptical cone
The surface area equation is:
Area = π * ( L * W / 4 + W * Z * Depth + (W / L) * (Z * Depth)^2 )
Where:
L = length of the main axis of the base
W = width of the minor axis of the base
Z = lateral slope (horizontal : vertical) of a vertical slice through the principal axis
- Parabolic -The storage unit is shaped like an elliptical paraboloid
The surface area equation is:
Area = (π / 4) * ( L * W / H) * Depth
Where:
L = length of the major axis at height H
W = width of the minor axis at height H
H = height
- Pyramid -This is for storage units in the shape of a truncated rectangular pyramid or rectangular box
The surface area equation is:
Area = L * W + 2 * (L + W) * Z * Depth +(2 * Z * Depth)^2
Where:
L = base length
W = base width
Z = side slope (horizontal/vertical) (which would be 0 for a box)
 Note: Read-only properties are intrinsic properties of the device, so the type change has to be done in Constructor.
Note: Read-only properties are intrinsic properties of the device, so the type change has to be done in Constructor.
 Note: You must click the
Note: You must click the
 at the top of the screen.
at the top of the screen.
If it is not visible, it means that the network is not enabled for SWMM. Enable it in your properties:
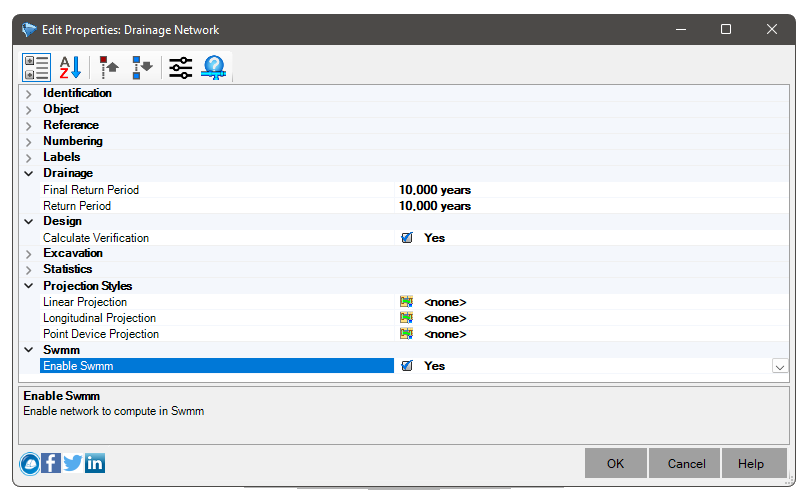


![]() Note: Read-only properties are intrinsic properties of the device, so the type change has to be done in Constructor.
Note: Read-only properties are intrinsic properties of the device, so the type change has to be done in Constructor.![]() Note: You must click the
Note: You must click the
![]() at the top of the screen.
at the top of the screen.
