 SWMM - LID Controls - Permeable Pavement
SWMM - LID Controls - Permeable Pavement
Permeable pavement - are excavated areas filled with gravel and paved with porous concrete or asphalt mix. Paving block systems consist of waterproof paving blocks placed on a bed of pea gravel or sand with a storage layer of gravel below

Schematically:
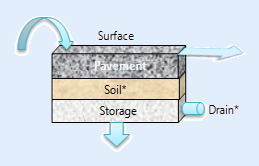
- SWMM
- Storage
- Storage Height - Gravel layer thickness or Rain Barrel height
- Clogging Factor - Total volume of treated runoff required to completely clog the bottom of the layer divided by the void volume of the layer
- Voice Index - The volume of void space in relation to the volume of solids in the layer
- Infiltration rate - The rate at which water penetrates the native soil below the layer
- Deep Drain
- drainage Coefficient - The drainage coefficient (C) and the exponent (n) determine the flow rate through a drain as a function of the height of the water stored above the drain displacement li>
- Control Curve - The name of an optional control curve that adjusts the calculated drain flow as a function of the head of water above the drain
- Exponent - The drainage coefficient (C) and exponent (n) determine the rate of flow through a drain as a function of the height of stored water above the drain displacement< b>q = C * h ^ n
- Opening Level - The height in the Drain's Storage Tier that causes the drain to automatically open when the water level rises above it.
- Closing Level - The height in the Drain Storage Tier that causes the drain to automatically close when the water level drops below it
- Offset - This is the height of the drain line above the bottom of a storage layer or rain barrel
- Wait Time - The number of hours of dry weather that must elapse before the drain line on a rain barrel opens
- Floor
- Floor Thickness - The volume of void space in relation to the volume of solids in the floor for continuous systems or for the fill material used in modular systems
- Clogging Factor - Number of void volumes of the treated runoff pavement layer that is required to completely clog the pavement
- Fraction Regenerated - The fractional degree to which pavement permeability is restored when a regeneration interval is reached
- Voice Index - The volume of void space in relation to the volume of solids in the floor for continuous systems or for the fill material used in modular systems
- Regeneration Interval - The number of days that the pavement layer can fill before its permeability is restored, normally by vacuuming its surface
- Permeability - Permeability of concrete or asphalt used in continuous systems or hydraulic Conductivity of filler material (gravel or sand) used in modular systems
- Impermeable Surface - Ratio of waterproof paving material to total area for modular systems
- Pollutant Removal - Specifies the removal rates for each pollutant
Note: Do not repeat the pollutant and do not leave the value at zero
- Soil
- Field Capacity - Volume of pore water in relation to total volume after soil drains completely
- Hydraulic Conductivity - Hydraulic Conductivity for fully saturated soil
- Conductivity Slope - Slope of the curve of log (Conductivity) versus soil moisture content (dimensionless)
- Thickness - Thickness of the soil layer
- Wilting Point - Volume of pore water in relation to total volume for a very dry soil, where only bound water remains
- Porosity - The volume of pore space in relation to the total soil volume
- Suction Potential - The average value of soil capillary suction along the wetting front
- Surface
- Vegetable Coverage - Vegetal Coverage
- Slope - Surface slope
- Side Slope - Slope of the side walls of a cross section of a ditch
- Storage Depth - Storage Depth
- Surface Roughness - Roughness

